共享内存
共享内存是效率最高的 IPC 通信方式,它的原理是 让不同进程的某些虚拟内存页对应同一个物理内存页。linux 系统中库文件经常使用共享内存以方便供不同进程调用,可以使用lsof命令进行查看。

在学习共享内存之前我们还需要了解一件事情——system V。
最早的时间 AT&T 公司中的贝尔实验室开发了Unix系统并公布出来使大家可以免费使用,但是在 AT&T 公司被美国的反垄断法拆成了两个公司以后就开始收费了;这个时候伯克利学校不干了,它发布了自己基于 Unix 的 BSD 版本。至此 Unix 就分裂了,其中一个是 system V 版本,其中一个是 BSD 版本。我接下来学习的就是 system V 的共享内存机制,其他也有 POSIX 版本的共享内存的机制,但是POSIX 版本的实现的太复杂了。
使用共享内存之前需要注意:
- 共享内存是不能跨越机器的,只能是同一台机器上的不同进程之间进行使用。
- 共享内存并没有像管道一样的阻塞机制,所以无法保证并发进程的运行结果正确。
相关函数
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id); // 可以将一个文件转换为system V IPC通信的key参数pathname 传入一个文件名,参数 proj_id 一般设置为 1
int shmget(key_t key, size_t size, int shmflg); // 创建共享内存size 为创建共享内存的大小,一般为页大小的整数倍(不够一页也会分配一页)
shmflg 描述生成的属性,当没有IPC_CREAT的时间程序会看有没有这个内存段如果没有就报错,当有IPC_CREAT的时间没有这个内存段就会创建内存段
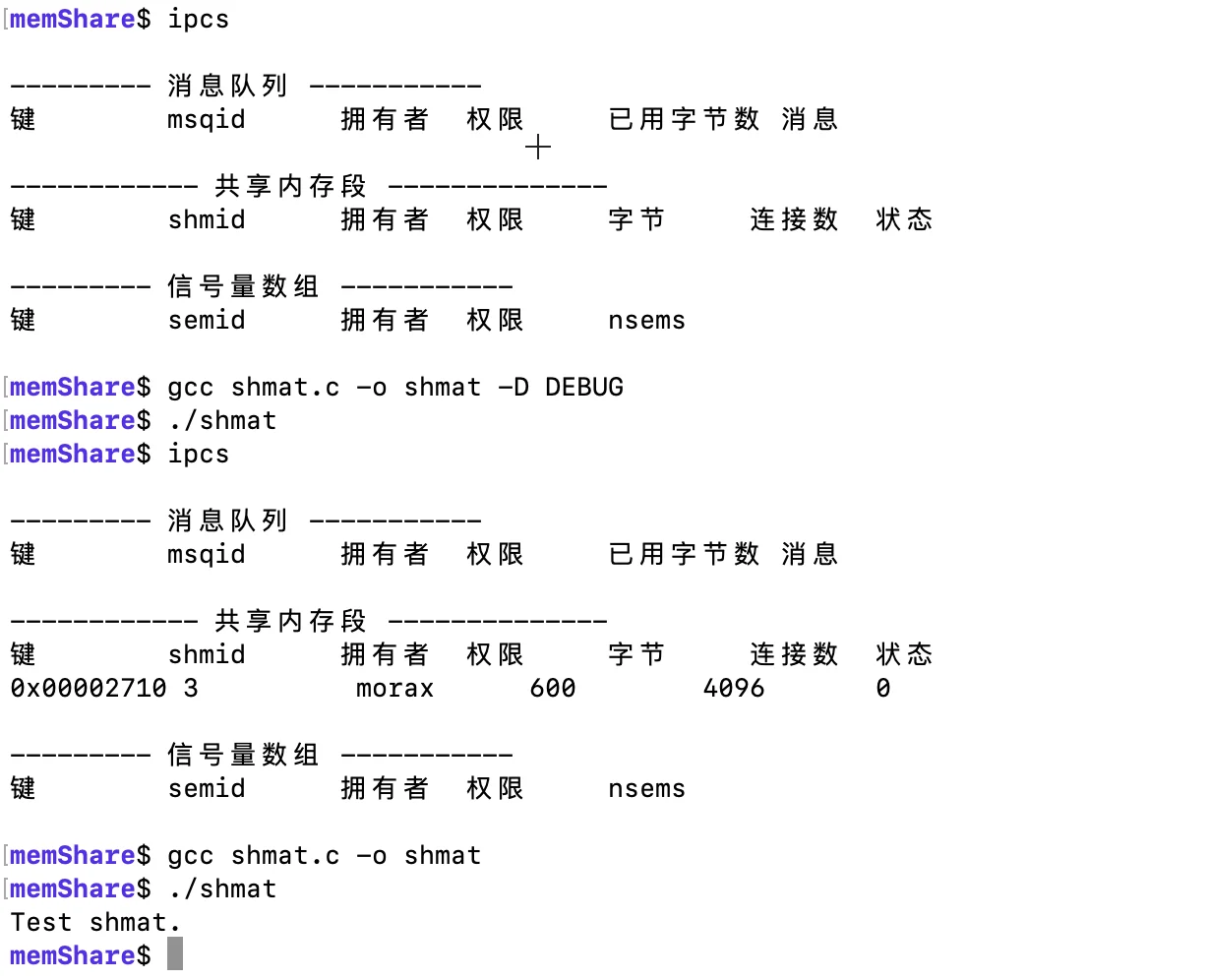
可以使用系统命令ipcs查看目前有哪些共享内存,使用ipcrm -M key 或者ipcrm -m shmid来删除已有的共享内存。
创建了共享内存之后还不能直接使用,因为我们写的程序只能访问虚拟内存并不能直接访问物理内存。接下来还需要将共享内存加载到虚拟内存中。
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *_Nullable shmaddr, int shmflg); // 第二个参数直接填NULL会自动分配虚拟内存空间并返回 当然你也可以自己malloc进行申请后传入,第三个参数直接填0
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr); // 回收创建的虚拟内存空间示例
最简单的使用同一个程序不同的条件编译来写和读同一块共享内存
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
/*
key_t key = ftok("file1", 1);
// int shmid = shmget(key,4096, IPC_CREAT); // 直接这样创建出来的共享内存权限是 0
int shmid = shmget(key,4096, IPC_CREAT|0600); // 可以 | 0600 来改变权限
*/
int shmid = shmget(10000, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0600);// 可以直接指定一个整数为key
if (shmid == -1) {
perror("shmget");
return -1;
}
char *p = (char *) shmat(shmid, NULL, 1);
#ifdef DEBUG
sprintf(p, "Test shmat.\n");
#else
printf("%s", p);
#endif
shmdt(p);
return 0;
}
接下来实现使用共享内存来完成父子间通信
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int shmid = shmget(10000, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0600);
if (shmid == -1) {
perror("shmget");
return -1;
}
char *p = (char *) shmat(shmid, NULL, 1);
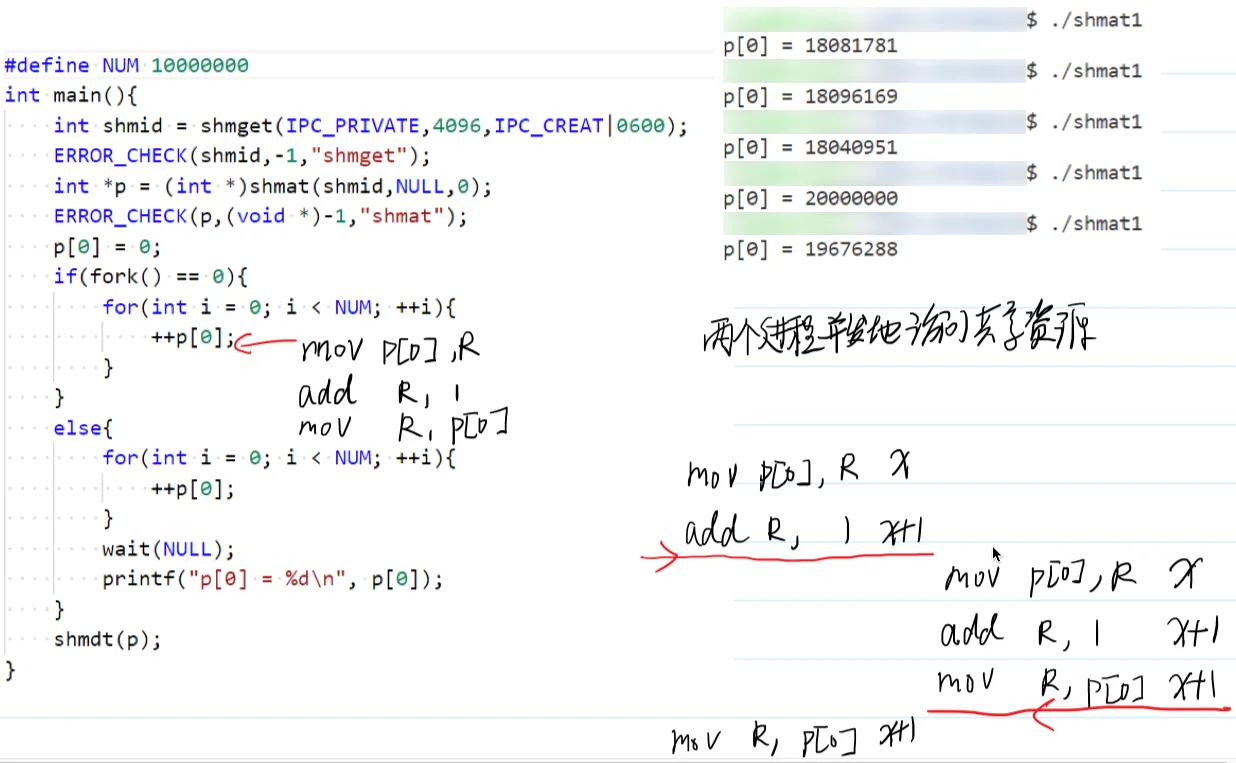
if (fork() == 0) {
sleep(1);
printf("%s", p);
} else {
strcpy(p, "Son, can you see my message?\n");
wait(NULL);
shmdt(p);
}
return 0;
}程序输出:
$ ./shmat1
Son, can you see my message?但是两个进程并发的访问共享内存资源也会导致程序出现一定的问题,程序并不能像我们预期的那样每次都输出正确的结果。导致程序有时出现错误的结果 因为并发的访问共享资源的时间不能保证原子操作,可能++操作并没有彻底完成该进程的CPU时间片就用完了,操作系统就切换其他进程来使用 CPU 时间片了,这就会导致程序得到错误的结果。
获取共享内存的状态
可以使用shmctl函数来获取共享内存的状态。但是这个函数设计的并不合格,它的设计违背了“单一职责”的原则(体现在第二个参数中),是典型的屎山代码。我们以后设计函数一定要避免出现类似的
#include <sys/shm.h>
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf);函数参数
shmid:使用创建共享内存时的返回值cmd:需要对共享内存进行的操作,可选值有IPC_STAT将与shmid相关的内核数据结构中的信息复制到buf指向的shmid_ds结构中。调用方必须对共享内存段具有读权限。IPC_SET将buf指向的shmid_ds结构的一些成员的值写入与此共享内存段相关的内核数据结构,同时更新其shm_ctime成员。可以更新如下字段:shm_perm_uid、shm_perm_gid以及shm_perm.mode的最小9位。调用进程的有效UID必须与共享内存段的所有者(shm_perm.uid)或创建者(shm_perm.cuid)匹配,否则调用者必须具有特权。IPC_RMID标记要销毁的段。只有在上一个进程分离该段之后(即相关结构shmid_ds的shm_nattch成员为0时),该段才会实际销毁。调用者必须是段的所有者或创建者,或具有特权。buf参数被忽略。如果段已标记为可销毁,则使用shm_perm的(非标准)SHM_DEST标志。将设置IPC_STAT检索的相关数据结构中的mode字段。调用者必须确保段最终被销毁;否则,发生异常的页将保留在内存或交换区中。
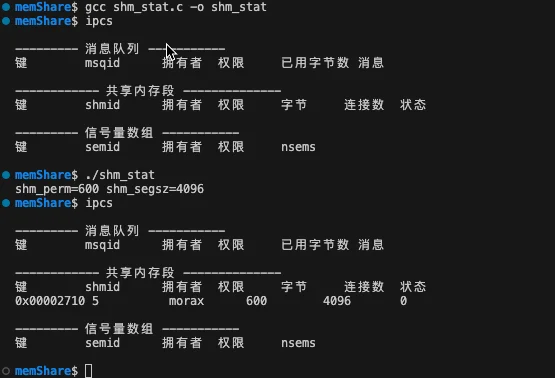
获取状态
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int shmid = shmget(10000, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0600);
if (shmid == -1)
{
perror("shmget");
return -1;
}
struct shmid_ds buf;
int statRet = shmctl(shmid, IPC_STAT, &buf);
if (statRet == -1)
{
perror("shmctl IPC_STAT");
return -1;
}
printf("shm_perm=%o shm_segsz=%lu\n", buf.shm_perm.mode, buf.shm_segsz);
return 0;
}
修改状态
修改状态的时间需要把结构体传递进去,但是我们一开始也不知道结构体里面都有哪些参数需要定义,所以我们需要先获取到结构体,然后对结构体进行修改,修改之后再进行传入
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int shmid = shmget(10000, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0600);
if (shmid == -1)
{
perror("shmget");
return -1;
}
struct shmid_ds buf;
int statRet = shmctl(shmid, IPC_STAT, &buf);
if (statRet == -1)
{
perror("shmctl IPC_STAT");
return -1;
}
buf.shm_perm.mode = 0666;
buf.shm_segsz = 8192;
statRet = shmctl(shmid, IPC_SET, &buf);
if (statRet == -1)
{
perror("shmctl IPC_STAT");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}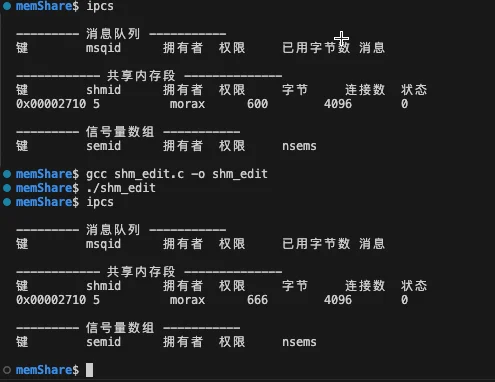
我们尝试对共享内存的权限和大小进行更改,但是可以看到对大小的更改并没有生效。
删除共享内存
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int shmid = shmget(10000, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0600);
if (shmid == -1)
{
perror("shmget");
return -1;
}
int statRet = shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);
if (statRet == -1)
{
perror("shmctl IPC_STAT");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}