操作文件
读取文件状态
c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);功能:获取文件状态信息。
参数:
path:文件名buf:保存文件信息的结构体
返回值:
- 成功:
0 - 失败:
-1
c
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; //文件的设备编号
ino_t st_ino; //节点
mode_t st_mode; //文件的类型和存取的权限
nlink_t st_nlink; //连到该文件的硬连接数目,刚建⽴的文件值为1
uid_t st_uid; //用户ID
gid_t st_gid; //组ID
dev_t st_rdev; //(设备类型)若此文件为设备文件,则为其设备编号
off_t st_size; //文件字节数(文件⼤⼩)
unsigned long st_blksize; //块⼤⼩(文件系统的I/O 缓冲区⼤⼩)
unsigned long st_blocks; //块数
time_t st_atime; //最后一次访问时间
time_t st_mtime; //最后一次修改时间
time_t st_ctime; //最后一次改变时间(指属性)
};c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char **args) {
if (argc < 2) return 0;
struct stat st = {0};
stat(args[1], &st);
int size = st.st_size;//得到结构体中的成员变量
printf("%d\n", size);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
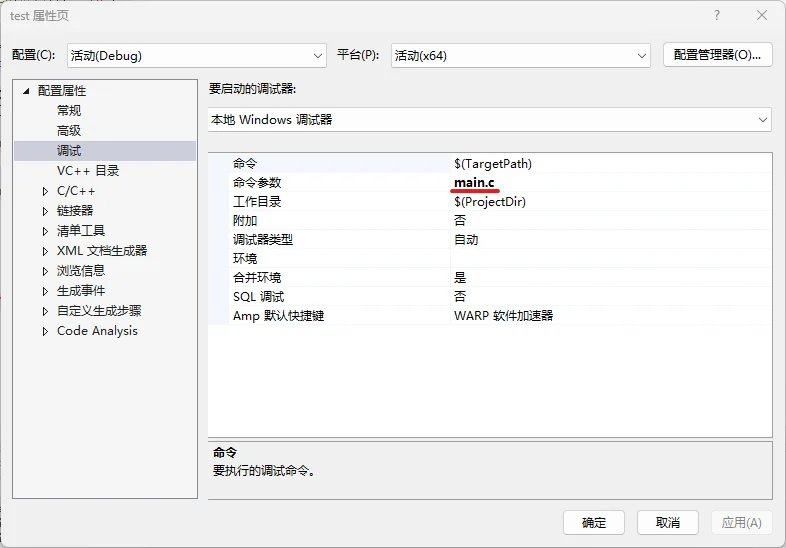
程序输出:
shell
342删除文件、重命名文件
c
#include <stdio.h>
int remove(const char *pathname);功能:删除文件。
参数:
pathname:文件名
返回值:
- 成功:
0 - 失败:
-1
c
#include <stdio.h>
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);功能:把oldpath的文件名改为newpath。
参数:
oldpath:旧文件名newpath:新文件名
返回值:
- 成功:
0 - 失败:
-1
文件读写案例
读写配置文件
配置文件格式如下:
正式的数据以 ‘:’冒号进行分割,冒号前为key起到索引作用,冒号后为value是实值。#开头的 为注释,而不是正式数据
点我查看代码
json
#英雄的Id
heroId:1
#英雄的姓名
heroName:德玛西亚
#英雄的攻击力
heroAtk:1000
#英雄的防御力
heroDef:500
#英雄的简介
heroInfo:前排坦克
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct ConfigInfo {
char key[64];
char value[64];
};
//获取文件有效行数
int getFileLine(const char *filePath) {
FILE *file = fopen(filePath, "r");
char buf[1024] = {0};
int lines = 0;
while (fgets(buf, 1024, file) != NULL) {
if (isValidLine(buf)) { lines++; }
memset(buf, 0, 1024);
}
fclose(file);
return lines;
}
//解析文件
void parseFile(const char *filePath, int lines, struct ConfigInfo **configInfo) {
struct ConfigInfo *pConfig = malloc(sizeof(struct ConfigInfo) * lines);
if (pConfig == NULL) { return; }
FILE *file = fopen(filePath, "r");
char buf[1024] = {0};
int index = 0;
while (fgets(buf, 1024, file) != NULL) {
if (isValidLine(buf)) {
//解析数据到struct ConfigInfo中
memset(pConfig[index].key, 0, 64);
memset(pConfig[index].value, 0, 64);
char *pos = strchr(buf, ':');
strncpy(pConfig[index].key, buf, pos - buf);
strncpy(pConfig[index].value, pos + 1, strlen(pos + 1) - 1);
// 从第二个单词开始截取字符串,并且不截取换行符
//printf("key = %s\n", pConfig[index].key);
//printf("value = %s\n", pConfig[index].value);
index++;
}
memset(buf, 0, 1024);
}
*configInfo = pConfig;
}
//获取指定的配置信息
char *getInfoByKey(char *key, struct ConfigInfo *configInfo, int lines) {
for (int i = 0; i < lines; i++) {
if (strcmp(key, configInfo[i].key) == 0) { return configInfo[i].value; }
}
return NULL;
}
//释放配置文件信息
void freeConfigInfo(struct ConfigInfo *configInfo) {
free(configInfo);
configInfo = NULL;
}
//判断当前行是否为有效行
int isValidLine(char *buf) {
if (buf[0] == '0' || buf[0] == '\0' || strchr(buf, ':') == NULL) {
return 0;// 如果行⽆限 返回假
}
return 1;
}
int main(void) {
char *filePath = "./config.txt";
int lines = getFileLine(filePath);
printf("文件有效行数为:%d\n", lines);
struct ConfigInfo *config = NULL;
parseFile(filePath, lines, &config);
printf("heroId = %s\n", getInfoByKey("heroId", config, lines));
printf("heroName: = %s\n", getInfoByKey("heroName", config, lines));
printf("heroAtk = %s\n", getInfoByKey("heroAtk", config, lines));
printf("heroDef: = %s\n", getInfoByKey("heroDef", config, lines));
printf("heroInfo: = %s\n", getInfoByKey("heroInfo", config, lines));
freeConfigInfo(config);
config = NULL;
return 0;
}