栈(Stack)
基本概念
概念:
首先它是一个线性表,也就是说,栈元素具有线性关系,即前驱后继关系。只不过它是一种特殊的线性表而已。定义中说是在线性表的表尾进行插入和删除操作,这里表尾是指栈顶,而不是栈底。
特性
操作
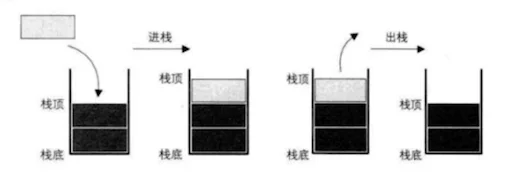
栈的插入操作,叫做进栈,也成压栈。类似子弹入弹夹(如下图所示)
栈的删除操作,叫做出栈,也有的叫做弾栈,退栈。如同弹夹中的子弹出夹(如下图所示)
顺序存储
基本概念
栈的顺序存储结构简称顺序栈,它是运算受限制的顺序表。顺序栈的存储结构是:利用一组地址连续的的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素,同时附设指针top只是栈顶元素在顺序表中的位置。
设计与实现
因为栈是一种特殊的线性表,所以栈的顺序存储可以通过顺序线性表来实现。通过数组来实现栈的顺序存储,栈顶为数组尾端。
C语言实现
#pragma once
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ERR_CHECK(lhs, rhs, errNum, msg, retVal) \
{ \
if (lhs == rhs) { \
errno = errNum; \
perror(msg); \
return retVal; \
} \
}#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
// 使用void*来防止用户直接获取到真实的栈结构体中的内容进行恶意操作
typedef void *Stack;
// 初始化栈,需指定栈的容量大小
Stack initStack(int capacity);
// 入栈
void pushStack(Stack s, void *data);
// 出栈并返回栈顶元素
void *popStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈顶元素
void *topStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈大小
int sizeStack(Stack s);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s);
// 销毁栈
void destoryStack(Stack s);#include "stack.h"
#include "errcheck.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义顺序栈的数据结构
typedef struct sstack {
void **pArr; // 底部数据结构为数组,可以容纳1024个元素
int capacity; // 栈的容量
int size; // 栈中元素个数
} SeqStack;
Stack initStack(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0 || capacity > 2048) {
ERR_CHECK(0, 0, EINVAL, "初始化栈失败,容量范围应为1-2048", NULL);
}
SeqStack *stk = malloc(sizeof(SeqStack));
ERR_CHECK(stk, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间失败", NULL);
stk->pArr = malloc(sizeof(void *) * capacity);
ERR_CHECK(stk->pArr, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间失败", NULL);
stk->capacity = capacity;
stk->size = 0;
return stk;
}
void pushStack(Stack s, void *data) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "插入失败,传入的栈为空", );
ERR_CHECK(data, NULL, EINVAL, "插入失败,传入的数据为空", );
SeqStack *stk = s;
ERR_CHECK(stk->size, stk->capacity, EUCLEAN, "插入失败,栈空间不足", );
stk->pArr[stk->size] = data;
++stk->size;
}
void *popStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "出栈失败,传入的栈为空", NULL);
SeqStack *stk = s;
return stk->pArr[stk->size--];
}
void *topStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈顶元素失败,传入的栈为空", NULL);
SeqStack *stk = s;
return stk->pArr[stk->size - 1];
}
int sizeStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈大小失败,传入的栈为空", -1);
SeqStack *stk = s;
return stk->size;
}
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "判断栈空失败,传入的栈为空指针", false);
SeqStack *stk = s;
return stk->size == 0;
}
void destoryStack(Stack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
return;
}
SeqStack *stk = s;
free(stk->pArr);
free(stk);
stk = NULL;
}#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct person {
char name[1024];
int age;
} Person;
int main(void) {
Stack stack = initStack(6);
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;
int f = 6;
int g = 7;
pushStack(stack, &a);
pushStack(stack, &b);
pushStack(stack, &c);
pushStack(stack, &d);
pushStack(stack, &e);
pushStack(stack, &f);
// pushStack(stack, &g); // 已经入栈了6个元素,再入栈会报错
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
popStack(stack);
pushStack(stack, &g);
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
popStack(stack);
popStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
Person p1;
p1.age = 12;
strcpy(p1.name, "小明");
Person p2;
p2.age = 11;
strcpy(p2.name, "小红");
pushStack(stack, &p1);
pushStack(stack, &p2);
Person *top = topStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top element name is %s, age is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), top->name, top->age);
popStack(stack);
top = topStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top element name is %s, age is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), top->name, top->age);
destoryStack(stack);
return 0;
}size is 6, and top is 6
size is 6, and top is 7
size is 4, and top is 4
size is 6, and top element name is 小红, age is 11
size is 5, and top element name is 小明, age is 12C++内置类型实现
#pragma once
// typedef int E;
typedef char E;
class Stack {
public:
Stack(int capacity = 10);
~Stack();
Stack(const Stack &s);
Stack &operator=(const Stack &s);
bool isEmpty() const;
bool isFull() const;
void push(const E &item);
E pop();
E top() const;
int size() const;
void clear();
private:
void expand();
private:
E *_pstack;
int _top;
int _capacity;
};#include "stack.h"
Stack::Stack(int capacity) : _pstack(new E[capacity]), _top(0), _capacity(capacity) {
}
Stack::~Stack() {
delete[] _pstack;
}
Stack::Stack(const Stack &s) : _top(s._top), _capacity(s._capacity) {
E *newStack = new E[_capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < s._top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = s._pstack[i];
}
_pstack = newStack;
}
bool Stack::isEmpty() const {
return _top == 0;
}
bool Stack::isFull() const {
return _top == _capacity;
}
void Stack::push(const E &item) {
if (isFull()) {
expand();
}
_pstack[_top++] = item;
}
E Stack::pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
E ret = _pstack[_top - 1];
--_top;
return ret;
}
E Stack::top() const {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
return _pstack[_top - 1];
}
int Stack::size() const {
return _capacity;
}
void Stack::clear() {
_top = 0;
}
void Stack::expand() {
int newCap = _capacity * 2;
E *newStack = new E[newCap];
for (int i = 0; i < _top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = _pstack[i];
}
delete[] _pstack;
_pstack = newStack;
_capacity = newCap;
}
Stack &Stack::operator=(const Stack &s) {
if (&s == this) {
return *this;
}
_top = s._top;
_capacity = s._capacity;
E *newStack = new E[_capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < s._top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = s._pstack[i];
}
_pstack = newStack;
return *this;
}stack size is 40
stack top is Z
stack s1 size is 40
stack s1 top is Z
stack s2 size is 40
stack s2 top is ZC++泛型实现
#pragma once
template <typename T>
class Stack {
public:
Stack(int capacity = 10) : _pstack(new T[capacity]), _top(0), _capacity(capacity) {
}
~Stack() { delete[] _pstack; }
Stack(const Stack &s) : _top(s._top), _capacity(s._capacity) {
T *newStack = new T[_capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < s._top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = s._pstack[i];
}
_pstack = newStack;
}
Stack &operator=(const Stack &s) {
if (&s == this) {
return *this;
}
_top = s._top;
_capacity = s._capacity;
T *newStack = new T[_capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < s._top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = s._pstack[i];
}
_pstack = newStack;
return *this;
}
bool isEmpty() const { return _top == 0; }
bool isFull() const { return _top == _capacity; }
void push(const T &item) {
if (isFull()) {
expand();
}
_pstack[_top++] = item;
}
T pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
T ret = _pstack[_top - 1];
--_top;
return ret;
}
T top() const {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
return _pstack[_top - 1];
}
int size() const { return _capacity; }
void clear() { _top = 0; }
private:
void expand() {
int newCap = _capacity * 2;
T *newStack = new T[newCap];
for (int i = 0; i < _top; ++i) {
newStack[i] = _pstack[i];
}
delete[] _pstack;
_pstack = newStack;
_capacity = newCap;
}
private:
T *_pstack;
int _top;
int _capacity;
};#include "stack.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
class Person {
public:
Person() {}
Person(std::string name, int age) : _name(name), _age(age) {}
std::string _name;
int _age;
};
int main() {
Stack<Person> s(2);
Person p1("zhangsan", 20);
Person p2("lisi", 21);
Person p3("wangwu", 22);
Person p4("xiaoming", 23);
Person p5("xiaohong", 24);
s.push(p1);
std::cout << "stack size is " << s.size()
<< ", ande top element name is " << s.top()._name
<< ", age is " << s.top()._age << std::endl;
s.push(p2);
s.push(p3);
s.push(p4);
s.push(p5);
std::cout << "stack size is " << s.size()
<< ", ande top element name is " << s.top()._name
<< ", age is " << s.top()._age << std::endl;
s.pop();
s.pop();
s.pop();
std::cout << "stack size is " << s.size()
<< ", ande top element name is " << s.top()._name
<< ", age is " << s.top()._age << std::endl;
Stack<Person> s1(s);
std::cout << "stack s1 size is " << s1.size()
<< ", ande top element name is " << s1.top()._name
<< ", age is " << s1.top()._age << std::endl;
return 0;
}stack size is 2, ande top element name is zhangsan, age is 20
stack size is 8, ande top element name is xiaohong, age is 24
stack size is 8, ande top element name is lisi, age is 21
stack s1 size is 8, ande top element name is lisi, age is 21链式存储
基本概念
栈的链式存储结构简称链栈。
思考如下问题:栈只是栈顶来做插入和删除操作,栈顶放在链表的头部还是尾部呢?
由于单链表有头指针,而栈顶指针也是必须的,那干嘛不让他俩合二为一呢,所以比较好的办法就是把栈顶放在单链表的头部。另外都已经有了栈顶在头部了,单链表中比较常用的头结点也就失去了意义,通常对于链栈来说,是不需要头结点的。
设计与实现
链栈是一种特殊的线性表,链栈可以通过链式线性表来实现。
#pragma once
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ERR_CHECK(lhs, rhs, errNum, msg, retVal) \
{ \
if (lhs == rhs) { \
errno = errNum; \
perror(msg); \
return retVal; \
} \
}#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
// 使用void*来防止用户直接获取到真实的栈结构体中的内容进行恶意操作
typedef void *Stack;
// 初始化栈
Stack initStack();
// 入栈
void pushStack(Stack s, void *data);
// 出栈并返回栈顶元素
void *popStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈顶元素
void *topStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈大小
int sizeStack(Stack s);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s);
// 销毁栈
void destoryStack(Stack s);#include "stack.h"
#include "errcheck.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node {
void *data; // 存储用户数据
struct node *next; // 指向下一个节点
} LkNode;
typedef struct lstack {
LkNode *head; // 头节点
int size; // 栈大小
} LkStack;
Stack initStack() {
LkStack *stk = malloc(sizeof(LkStack));
ERR_CHECK(stk, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(stk->head, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head->next = NULL;
stk->size = 0;
return stk;
}
void pushStack(Stack s, void *data) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "入栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", );
ERR_CHECK(data, NULL, EINVAL, "入栈失败,传入的数据为空指针", );
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *node = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(node, NULL, ENOMEM, "入栈失败,申请节点空间出错", );
node->data = data;
node->next = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = node;
++stk->size;
}
void *popStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "出栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", NULL);
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *retNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = retNode->next;
--stk->size;
void *retData = retNode->data;
free(retNode);
return retData;
}
void *topStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈顶元素失败,传入的栈为空指针", NULL);
LkStack *stk = s;
ERR_CHECK(stk->size, 0, ERANGE, "获取栈顶元素失败,栈为空", NULL);
return stk->head->next->data;
}
int sizeStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈大小失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size;
}
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "栈指针为空", true);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size == 0;
}
void destoryStack(Stack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
return;
}
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *curNode = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < stk->size; ++i) {
curNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = curNode->next;
free(curNode);
}
free(stk->head);
stk->head = NULL;
free(stk);
stk = NULL;
}#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct person {
char name[1024];
int age;
} Person;
int main(void) {
Stack stack = initStack(6);
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;
int f = 6;
int g = 7;
pushStack(stack, &a);
pushStack(stack, &b);
pushStack(stack, &c);
pushStack(stack, &d);
pushStack(stack, &e);
pushStack(stack, &f);
// pushStack(stack, &g); // 已经入栈了6个元素,再入栈会报错
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
popStack(stack);
pushStack(stack, &g);
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
popStack(stack);
popStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), *((int *)topStack(stack)));
Person p1;
p1.age = 12;
strcpy(p1.name, "小明");
Person p2;
p2.age = 11;
strcpy(p2.name, "小红");
pushStack(stack, &p1);
pushStack(stack, &p2);
Person *top = topStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top element name is %s, age is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), top->name, top->age);
popStack(stack);
top = topStack(stack);
printf("size is %d, and top element name is %s, age is %d\n", sizeStack(stack), top->name, top->age);
destoryStack(stack);
return 0;
}size is 6, and top is 6
size is 6, and top is 7
size is 4, and top is 4
size is 6, and top element name is 小红, age is 11
size is 5, and top element name is 小明, age is 12应用案例
就近匹配
几乎所有的编译器都具有检测括号是否匹配的能力,那么如何实现编译器中的符号成对检测?如字符串: 5+5*(6)+9/3*1)-(1+3(
算法思路
从第一个字符开始扫描,当遇见普通字符时忽略,当遇见左括号时压入栈中,当遇见右括号时从栈中弹出栈顶符号,并进行匹配
- 匹配成功:继续读入下一个字符
- 匹配失败:立即停止,并报错
扫描结束
- 成功: 所有字符扫描完毕,且栈为空
- 失败:匹配失败或所有字符扫描完毕但栈非空
点击查看代码
栈的代码直接复用链式栈的代码,解题代码如下
#include "stack.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void) {
const char *str = "5+5*(6)+9/3*1)-(1+3(";
Stack stack = initStack();
int len = strlen(str);
char c;
char left = '(';
char right = ')';
bool flag = true;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
c = str[i];
if (c == left) {
pushStack(stack, &left);
} else if (c == right) {
if (isEmptyStack(stack)) {
flag = false;
break;
}
popStack(stack);
}
}
if (flag && isEmptyStack(stack)) {
printf("匹配成功\n");
} else {
printf("匹配失败\n");
}
return 0;
}总结
- 当需要检测成对出现但又互不相邻的事物时可以使用栈“后进先出”的特性
- 栈非常适合于需要“就近匹配”的场合
中缀表达式和后缀表达式
后缀表达式(由波兰科学家在20世纪50年代提出):将运算符放在数字后面 —> 符合计算机运算。我们习惯的数学表达式叫做中缀表达式 —> 符合人类思考习惯。实例
5 + 4 --> 5 4 +1 + 2 * 3 --> 1 2 3 * +8 +( 3 – 1 ) * 5 --> 8 3 1 – 5 * +
中缀转后缀算法:
遍历中缀表达式中的数字和符号:对于数字直接输出,对于符号
- 左括号:进栈
- 运算符号:与栈顶符号进行优先级比较
- 若栈顶符号优先级低:此符号进栈(默认栈顶若是左括号,左括号优先级最低)
- 若栈顶符号优先级不低:将栈顶符号弹出并输出,之后进栈
- 右括号:将栈顶符号弹出并输出,直到匹配左括号,将左括号和右括号同时舍弃
遍历结束:将栈中的所有符号弹出并输出
动手练习
将我们喜欢的读的中缀表达式转换成计算机喜欢的后缀表达式
中缀表达式: 8 + ( 3 – 1 ) * 5
后缀表达式: 8 3 1 – 5 * +
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ERR_CHECK(lhs, rhs, errNum, msg, retVal) \
{ \
if (lhs == rhs) { \
errno = errNum; \
perror(msg); \
return retVal; \
} \
}#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
// 使用void*来防止用户直接获取到真实的栈结构体中的内容进行恶意操作
typedef void *Stack;
// 初始化栈
Stack initStack();
// 入栈
void pushStack(Stack s, char data);
// 出栈并返回栈顶元素
char popStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈顶元素
char topStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈大小
int sizeStack(Stack s);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s);
// 销毁栈
void destoryStack(Stack s);#include "stack.h"
#include "errcheck.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node {
char data; // 存储用户数据
struct node *next; // 指向下一个节点
} LkNode;
typedef struct lstack {
LkNode *head; // 头节点
int size; // 栈大小
} LkStack;
Stack initStack() {
LkStack *stk = malloc(sizeof(LkStack));
ERR_CHECK(stk, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(stk->head, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head->next = NULL;
stk->size = 0;
return stk;
}
void pushStack(Stack s, char data) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "入栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", );
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *node = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(node, NULL, ENOMEM, "入栈失败,申请节点空间出错", );
node->data = data;
node->next = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = node;
++stk->size;
}
char popStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "出栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *retNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = retNode->next;
--stk->size;
char retData = retNode->data;
free(retNode);
return retData;
}
char topStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈顶元素失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
ERR_CHECK(stk->size, 0, ERANGE, "获取栈顶元素失败,栈为空", -1);
return stk->head->next->data;
}
int sizeStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈大小失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size;
}
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "栈指针为空", true);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size == 0;
}
void destoryStack(Stack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
return;
}
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *curNode = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < stk->size; ++i) {
curNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = curNode->next;
free(curNode);
}
free(stk->head);
stk->head = NULL;
free(stk);
stk = NULL;
}#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void convert(const char *str) {
Stack stk = initStack();
int len = strlen(str);
char c;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
c = str[i];
if (c == ' ') {
continue;
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
printf("%c ", c);
} else if (c == '(') {
pushStack(stk, '(');
} else if (c == ')') {
char top = popStack(stk);
if (top == '(') {
continue;
} else {
while (top != '(') {
printf("%c ", top);
top = popStack(stk);
}
}
} else {
char top = ' ';
if (!isEmptyStack(stk)) {
top = topStack(stk);
}
if (top == '(') {
pushStack(stk, c);
} else {
if (c == '+' || c == '-') {
if (top != ' ') {
top = popStack(stk);
printf("%c ", top);
}
pushStack(stk, c);
} else {
pushStack(stk, c);
}
}
}
}
int size = sizeStack(stk);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
char top = popStack(stk);
printf("%c ", top);
}
putchar('\n');
destoryStack(stk);
}
int main(void) {
convert("5 + 4");
convert("1 + 2 * 3");
convert("8 +( 3 - 1 ) * 5");
return 0;
}5 4 +
1 2 3 * +
8 3 1 - 5 * +基于后缀表达式计算
思考:计算机是如何基于后缀表达式计算的?
例如:8 3 1 – 5 * +
计算规则
遍历后缀表达式中的数字和符号。对于数字直接进栈,对于符号
- 从栈中弹出右操作数
- 从栈中弹出左操作数
- 根据符号进行运算
- 将运算结果压入栈中
遍历结束:栈中的唯一数字为计算结果
点击查看代码
#pragma once
#include <errno.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ERR_CHECK(lhs, rhs, errNum, msg, retVal) \
{ \
if (lhs == rhs) { \
errno = errNum; \
perror(msg); \
return retVal; \
} \
}#pragma once
#include <stdbool.h>
// 使用void*来防止用户直接获取到真实的栈结构体中的内容进行恶意操作
typedef void *Stack;
// 初始化栈
Stack initStack();
// 入栈
void pushStack(Stack s, int data);
// 出栈并返回栈顶元素
int popStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈顶元素
int topStack(Stack s);
// 返回栈大小
int sizeStack(Stack s);
// 判断栈是否为空
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s);
// 销毁栈
void destoryStack(Stack s);#include "stack.h"
#include "errcheck.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct node {
int data; // 存储用户数据
struct node *next; // 指向下一个节点
} LkNode;
typedef struct lstack {
LkNode *head; // 头节点
int size; // 栈大小
} LkStack;
Stack initStack() {
LkStack *stk = malloc(sizeof(LkStack));
ERR_CHECK(stk, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(stk->head, NULL, ENOMEM, "初始化栈失败,申请空间出错", stk);
stk->head->next = NULL;
stk->size = 0;
return stk;
}
void pushStack(Stack s, int data) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "入栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", );
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *node = malloc(sizeof(LkNode));
ERR_CHECK(node, NULL, ENOMEM, "入栈失败,申请节点空间出错", );
node->data = data;
node->next = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = node;
++stk->size;
}
int popStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "出栈失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *retNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = retNode->next;
--stk->size;
int retData = retNode->data;
free(retNode);
return retData;
}
int topStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈顶元素失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
ERR_CHECK(stk->size, 0, ERANGE, "获取栈顶元素失败,栈为空", -1);
return stk->head->next->data;
}
int sizeStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "获取栈大小失败,传入的栈为空指针", -1);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size;
}
bool isEmptyStack(Stack s) {
ERR_CHECK(s, NULL, EINVAL, "栈指针为空", true);
LkStack *stk = s;
return stk->size == 0;
}
void destoryStack(Stack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
return;
}
LkStack *stk = s;
LkNode *curNode = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < stk->size; ++i) {
curNode = stk->head->next;
stk->head->next = curNode->next;
free(curNode);
}
free(stk->head);
stk->head = NULL;
free(stk);
stk = NULL;
}#include "stack.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void convert(const char *str, char *retStr) {
Stack stk = initStack();
int len = strlen(str);
int retLen = strlen(retStr);
char c;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
c = str[i];
if (c == ' ') {
continue;
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
retLen = strlen(retStr);
retStr[retLen] = c;
retStr[retLen + 1] = ' ';
} else if (c == '(') {
pushStack(stk, '(');
} else if (c == ')') {
char top = popStack(stk);
if (top == '(') {
continue;
} else {
while (top != '(') {
retLen = strlen(retStr);
retStr[retLen] = top;
retStr[retLen + 1] = ' ';
top = popStack(stk);
}
}
} else {
char top = ' ';
if (!isEmptyStack(stk)) {
top = topStack(stk);
}
if (top == '(') {
pushStack(stk, c);
} else {
if (c == '+' || c == '-') {
if (top != ' ') {
top = popStack(stk);
retLen = strlen(retStr);
retStr[retLen] = top;
retStr[retLen + 1] = ' ';
}
pushStack(stk, c);
} else {
pushStack(stk, c);
}
}
}
}
int size = sizeStack(stk);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
char top = popStack(stk);
retLen = strlen(retStr);
retStr[retLen] = top;
retStr[retLen + 1] = ' ';
}
destoryStack(stk);
}
int compute(const char *str) {
int retNum = 0;
int len = strlen(str);
char c;
Stack stk = initStack();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
c = str[i];
if (c == ' ') {
continue;
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
pushStack(stk, c - 48);
} else {
int rhs = popStack(stk);
int lhs = popStack(stk);
int result = 0;
if (c == '+') {
result = lhs + rhs;
} else if (c == '-') {
result = lhs - rhs;
} else if (c == '*') {
result = lhs * rhs;
}
pushStack(stk, result);
}
}
retNum = popStack(stk);
destoryStack(stk);
return retNum;
}
int main(void) {
char str1[1024] = {0};
convert("5 + 4", str1); // 9
char str2[1024] = {0};
convert("1 + 2 * 3", str2); // 7
char str3[1024] = {0};
convert("8 +( 3 - 1 ) * 5", str3); // 18
printf("%s\n", str1);
printf("%d\n", compute(str1));
printf("%s\n", str2);
printf("%d\n", compute(str2));
printf("%s\n", str3);
printf("%d\n", compute(str3));
return 0;
}5 4 +
9
1 2 3 * +
7
8 3 1 - 5 * +
18